 |
Colour Image Processing
(Elective Course for M. Techs) |
Colour Image Processing
|
 |
Syllabus
I. Colour Science | |
Electromagnetic radiation, Spectral Power Distribution Functions (SPDFs), Colour by Emission, Absorption, Dispersion and Transmission. |
|
Structure of the retina, SML Cones, Optical Pathway, Colour Theories. |
|
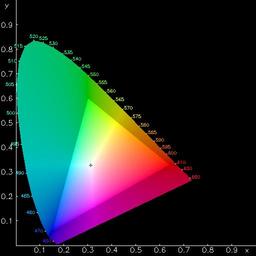
CIE Colour Matching Experiment, XYZ Tristimulus model, x-y chromaticity diagram, MacAdam ellipses, CIE Lab space. |
|
Colour gamut, RGB, CMY(K), HSV, Luv and other spaces, Interconversion between different spaces. |
|
II. Colour Processing | |
Colour Negatives, Thresholding and Binarization, Ranging and Colour Filters, Colour Image Enhancement and Filtering, Colour contrast |
|
Vector Representation, Ordering Relationships, Noise Removal using Vector Filters, Vector Edge Detection, Canny and Cumani operations |
|
III. Colour Printing and Rendering | |
Dithering, random, dispersed dot and clustered dot dithering, blue and pink noise, colour screens, colour dithering |
|
Error diffusion, Floyd-Steinberg and other algorithms, comparison with dithering |
|
Single-sensor colour cameras, Bayer Colour Filter Array, demosaicking |
|
III. Applications | |
Image tampering, colour matching, JPEG block inconsistency, lighting inconsistencies, recognizing laser, inkjet printing and colour photocopies |
|
Physical processes and colour changes |
Material shown in classes |
Major types of colour blindness: protanopia and deuteranopia, simulating colour impaired vision |
|
Experiments
SPDF
and Colour
Python code of SPDF and Colour
Python Utility Modules
Data Files
Just for Fun!
Given here is a photo published in the The Hindu newspaper dated